 The applications of an Android smartphone, starting from the first time they are started, create a cache on the memory and a series of internal data.
The applications of an Android smartphone, starting from the first time they are started, create a cache on the memory and a series of internal data.Therefore, by opening the Android settings and going to the Applications section to see All the internet and downloaded apps, you can see the indication of the space occupied by these in the internal memory or SD card.
You will notice, in the list, that the size of almost all applications is much higher than expected and compared to when they were downloaded.
For example, Facebook and Google apps could be as large as 200 MB while for apps like Google Play Services, Chrome, Google Maps, Youtube and many others.
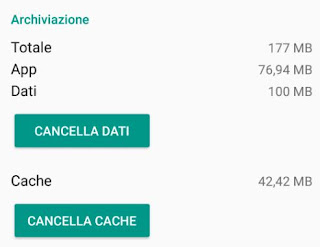
By tapping on an app, you can then tap on Memory to see a detail on how this figure relating to the occupied memory size is formed, which includes the application and then the files in the Cache and the Data.
From here you can then press the keys to clear the cache and clear the data, and it is useful as well as interesting to understand what is the difference and what it means to clear Cache and Data.
NOTE: In some smartphones updated to Android 11 or later, the cache removal option does not exist in the Storage Space menu. Instead, you will find a list of data categories, from which you can free up memory by clearing the cache and storage space for each individual app.
1) Clear the Android Cache
The Cache is made up of files created by the application during its use, which however do not affect its operation.
For example, an app like Chrome caches images downloaded from the internet so you don't have to re-download them when you visit a certain website for the second time, while the Facebook app downloads photos of people whose profile you peek at.
This operation allows the smartphone to save internet traffic unnecessarily.
To recover memory space in Android, one of the first tips is to clear the application cache.
There are no consequences to this action, except that the app opens the contents already viewed more slowly than before, because it has to re-download them from the internet.
Clearing the cache is also a useful action when the app seems out of sync or when it seems to have problems or even when it gets slow.
Android (up to Android 10 version) also allows you to clearing the application cache all at once.
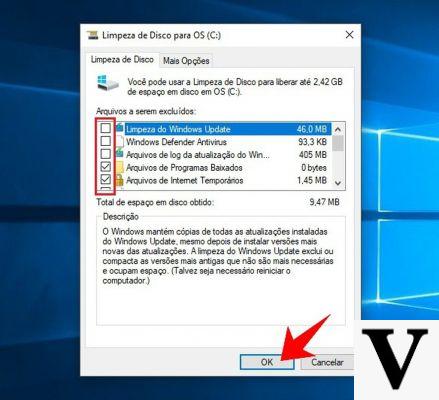
To do this you need to go to Settings and then to Archiving, tap on Cached data and press OK when asked if you want to clear the Android cache.
On some phones the menu may have a different name, for example Memory or Storage space.
As already seen, there are Apps to clear all Android cache to recover memory even faster and with more options to choose which apps you want to delete.
2) Delete App Data or Android Storage Space
While the cache includes files saved by the application while in use, but which are not part of the app itself, and Dati (since Android 11 it is called Storage space) are fundamental.
Data includes changes to settings and credentials including account passwords to access apps.
In games, Data includes progress made and saved games, in Google Translate the saved languages to work offline while in Google Maps the saved maps and so on.
By clearing an app's data, it is completely reset as if it had just been installed.
It is therefore a complete reset of the application.
If you delete App data such as Facebook, you must then log in again with the account and reconfigure the various customized options.
Clearing app data is useful when that application no longer works, gives errors, or closes by itself.
For example, when the Google Play Store is not working or if there are errors with Google Play Services, the solution is to clear the data of these apps.
Note that App Data and Cache are always stored in the phone's internal memory so even if you can move apps to the SD card, you cannot also move Data and Cache without rooting the phone.